Promotional Features
New Fiber-Interlaced Liposomal encapsulation increases superior berberine enhancements
Traditional medicine and therapeutics lend significant contributions to proactive healthcare.
With documented roots tracing back centuries, both practices aim to unlock the advantages of botanical compounds. Yet, experiencing the full potential of their therapeutic benefits is anything but straightforward. The efficacy of traditional remedies hinges on pivotal factors such as bioavailability, stability and release kinetics. For botanicals with inherently low bioavailability, realizing the minimum effective concentration often necessitates administering substantial doses which proves undesirable for consumers.
Berberine's bioavailability challenge
Berberine, an alkaloid derived from plants and found in numerous medicinal herbs, boasts a diverse pharmacological portfolio. This botanical compound exhibits an impressive array of health-enhancing attributes, including antioxidation, anti-inflammation, antitumor potential, antimicrobial properties, hepatoprotection, hypolipidemic effects, and the ability to lower blood sugar levels.1,2
However, berberine’s notably low oral bioavailability presents a substantial limitation to realizing the compound's therapeutic potential. When administered orally, berberine’s passage through the gastrointestinal tract encounters acidic environments which initiate enzymatic degradation and poor absorption.
The limitations of conventional liposomes
In such cases of low bioavailability it is well established that liposomes may be utilized.
Liposomes – spherical vesicles composed of lipid bilayers – serve as delivery vehicles, uniquely equipped to shield active compounds from degradation and facilitate controlled, sustained release. Their structural resemblance to cell membrane lipid bilayers provides them with the capacity for efficient uptake and targeted delivery of therapeutic agents.
However, although they are largely preferred, certain aspects of conventional liposomal formulations may impact the therapeutic effect of active biomolecules leading to impaired bioavailability, thus invalidating their intended use. Furthermore, stability of the active molecules within the conventional liposome for prolonged duration is also debatable.
A novel approach: fiber-interlaced liposomal formulations
Vidya Herbs, a world-renowned manufacturer of plant extracts, observed a more effective alternative to conventional liposomes. The improved method encapsulates active biomolecules in the core of the liposome with plant-based fibers embedded into the exterior. The cross-linking of fibers with lecithin shelters the biomolecules from leaching the active core in addition to providing a more stable structure.
Realizing the potential and merits of plant fiber encapsulation, Vidya Herbs has developed a patent-pending technology that enhances stability, optimizes bioavailability, sustains release, and provides a higher load capacity. FIL Technology™ (Fiber-Interlaced Liposomal) converts the liquid liposomes to a novel stabilized form of powdered liposomes.
The core structure of the liposome has an extra layer of protection because of the plant-fiber cross layer on the exterior. Encapsulation of biomolecules like berberine with the FIL Technology™ is a novel strategy to enhance the stability, bioavailability, release time and the loading of liposomes through the reinforcement of fibers with lecithin.
The innovation of FIL Technology™ represents a leap forward in liposomal delivery systems. By encapsulating berberine within the core of liposomes and fortifying the liposome's structure with plant-based fibers, FIL Technology™ overcomes many of the limitations associated with conventional liposomes.
A comparative pharmacokinetic study
To establish the superiority of berberine using FIL Technology™, Vidya Herbs designed a comparative pharmacokinetic study of the berberine formulation FIL Technology™ berberine, not less than (NLT) 45% berberine and unformulated berberine (88% berberine hydrogen chloride HCl).
The relative release profile
The in vitro release profile and the oral bioavailability of FIL Technology™ berberine in comparison to the unformulated berberine, was evaluated in male Wistar rats. Rats in each of the experimental group received a single oral dose of FIL Technology™ berberine (600 mg/kg), while those in the control group received an equivalent dose of unformulated berberine HCl (320 mg/kg). Quantification of berberine in the blood samples was performed using the liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LCMS) method. Pharmacokinetic analysis was performed using R statistical software (Version 4.5).
Research results: Comparative analysis of in vitro release
There was a marked increase in the cumulative amount of berberine released from the control group with unformulated berberine up to six hours. Whereas a sustained and controlled release of berberine was seen in the FIL Technology™ berberine formulation. After a period of six hours, 48.52% berberine was released from FIL Technology™ formulation whereas in the unformulated berberine the cumulative release reached 100%. The data is presented as mean and standard deviation (SD) of three independent experiments.
Figure 1. Relative release profile of berberine from the FIL Technology™ formulation and control (Unformulated) samples reflecting a sustained release pattern of Berberine from the FIL Technology™ formulation.
Pharmacokinetic study of FIL Technology™ Formulated and Unformulated Berberine
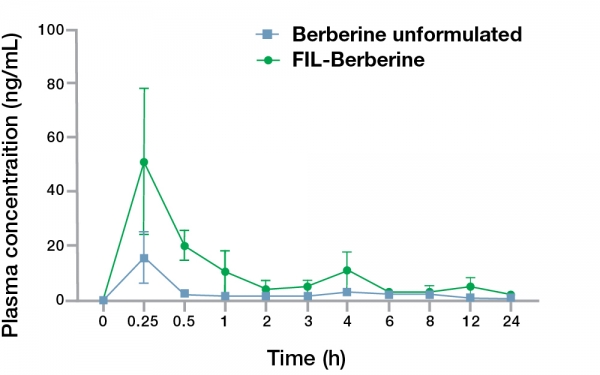
The concentration-time curve of berberine after oral administration in rats revealed that the mean plasma concentration (Cmax) of berberine in the FIL Technology™ formulation reached a maximum value of 50.98±27.03 ng/mL and time to peak drug concentration (Tmax) of 0.25±0.00 h. In comparison, the unformulated berberine showed the Cmax of 15.54±9.66 ng/mL and Tmax of 0.25±0.00 h. The FIL Technology™ berberine administered group showed a higher half-life (t1/2) of 7.90±1.58 h when compared with the unformulated berberine group that exhibited a t1/2 of 7.32±0.61 h.
A similar trend was also observed in the area under the curve (AUC) of FIL Technology™ berberine that was higher than the unformulated berberine. The data demonstrates that the oral bioavailability of FIL Technology™ berberine is 3.37-fold higher than unformulated berberine HCl in Wistar rats.
Figure 2. 24-hour concentration-time kinetics of berberine plasma concentrations after a single dose oral administration of FIL Technology™ berberine.
The future promise of FIL Technology™
In summation, the introduction of Vidya Herbs’ FIL Technology™ represents a significant stride forward. FIL Technology™ improves the sustained release pattern of berberine in addition to providing a longer bioavailability percentage than unformulated berberine. The oral bioavailability of FIL Technology™ berberine is remarkably 3.37-fold higher than unformulated berberine HCl.
In addition, the data makes it clear that FIL Technology™ is a superior form of liposomal use with the potential to further unlock the therapeutic delivery of various fat-soluble actives and botanicals. In accordance with these positive findings, Vidya Herbs plans to conduct human efficacy trials with curcumin, saw palmetto, Coenzyme Q10, vegan omega 3, and ashwagandha.
References
1. Wang, K.; Feng, X.; Chai, L.; et al. (2017). The metabolism of berberine and its contribution to the pharmacological effects. Drug Metabolism Reviews. 49(2), 139–157.
2. Wang, S., Ren, H., Zhong, H., et al. (2022). Combined berberine and probiotic treatment as an effective regimen for improving postprandial hyperlipidemia in type 2 diabetes patients: a double blinded placebo controlled randomized study. Gut microbes. 14(1), 2003176.